11. IO
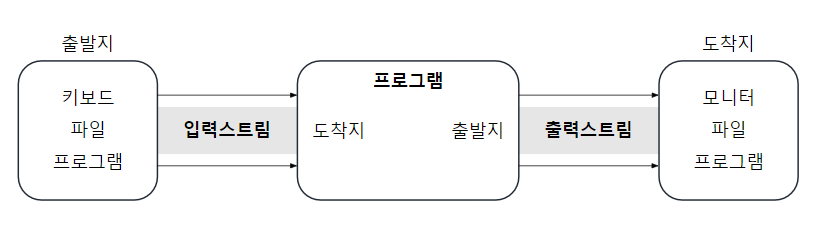
입출력
1) 입출력
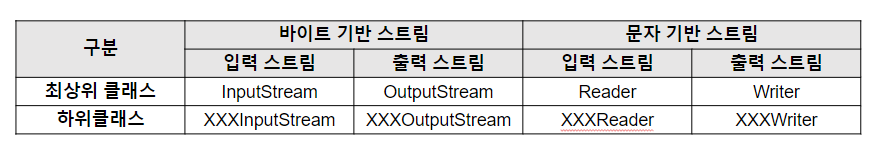
2) 스트림(Stream) 클래스
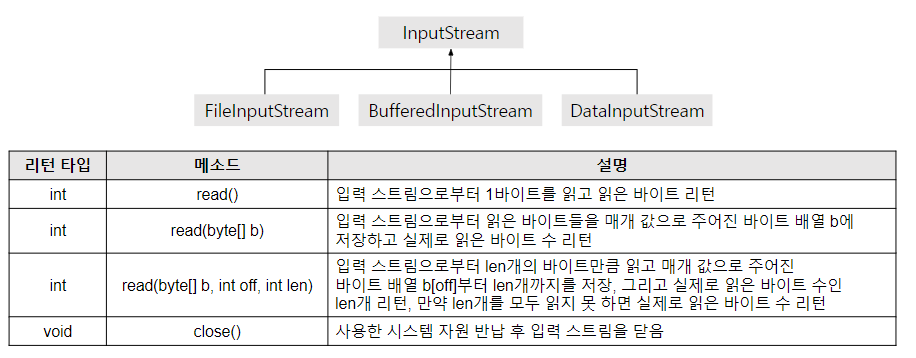
3) InputStream
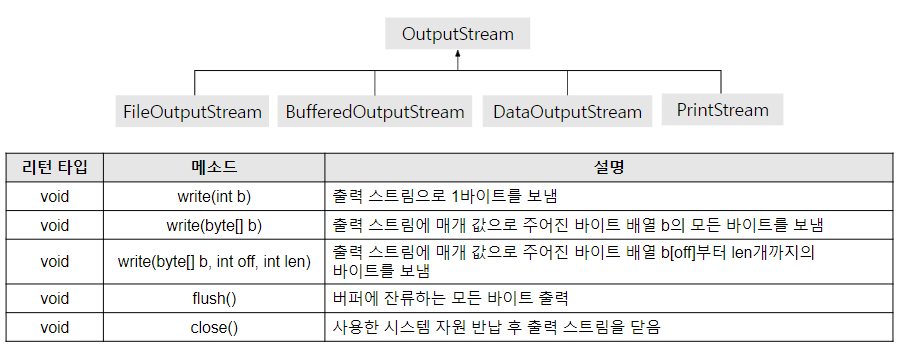
4) OutputStream
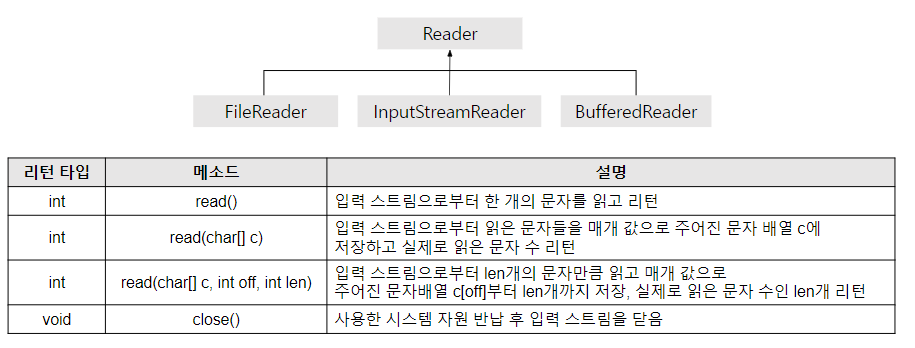
5) Reader
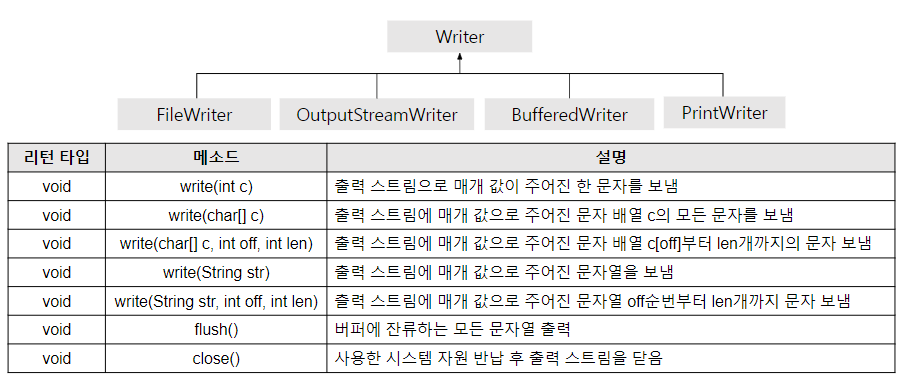
6) Writer
7) 사용예시
- 파일로 사용하려는 프로젝트에서 새로만들기 하여 General 폴더의 file을 만들어준다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
< 바이트 기반 OutputStream >
// FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test1.txt");
// 이렇게 하면 FileNotFoundException 예외 발생. 예외 처리 필요
// -> 파일로 만들어지기 전에 예외발생하여 종료 될 수 있다는 예외
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("test1.txt");
// 현재 프로그램에서 test1.txt 파일로 출력하는 통로 객체 생성
// 이 파일은 목적지가 필요하고 현재 현재 해당 12_IO 프로젝트 폴더가 기본 목적지로 설정
String str = "Hello";
for( int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){
fos.write(str.charAt(i));
// write는 IOException을 발생. 예외처리 필요
}
} catch (IOException e){
// FileNotFoundException은 IOException의 자손이므로
// 다형성에 의해 IOException로 둘 다 잡을 수 있다
e.printStackTrace(); // 예외 추적 후 출력
} finally {
// 쓸데없는 통로 지우기, 메모리 관리 차원 --> 필수작성
try{
fos.close();
// 통로 닫는 메소드도 예외 발생하므로 예외처리 해주기
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
< 바이트 기반 InputStream >
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
tis = new FileInputStream("test1.txt");
// FileInputStream은 1byte씩만 읽어올 수 있다
while(true){
int data = fis.read();
// 다음 1byte를 읽어오는 정수형 반환타입의 메소드. 유니코드 정수
// 다음 내용이 없으면 -1 반환
if( data == -1 ) break;
System.out.print( (char)data );
}
} catch ( IOException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
< 문자 기반 OutputStream >
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("test1.txt");
// 매개변수로 true를 추가하면 실행한만큼 연속으로 작성된다. ("test1.txt", true);
String str = "안녕하세요. Hello. 1234. !#";
fw.write(str);
} catch ( IOException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
< 문자 기반 InputStream >
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("test1.txt");
while(true){
int data = fr.read();
// 다음 문자 읽어옴. 없으면 -1
if( data == -1 ) break;
System.out.print( (char)data );
}
} catch ( IOException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}