01.Spring Security
Spring Security
- 인증 방식에는
- credential 방식 : username, password를 이용하는 방식
- 이중 인증(twofactor 인증) : 사용자가 입력한 개인 정보를 인증 후, 다른 인증 체계(예 : 물리적인 카드)를 이용하여 두가지의 조합으로 인증하는 방식
- 하드웨어 인증 : 자동차 키와 같은 방식
- Spring Security는 credential 기반의 인증이다.
- principa : 아이디(username)
- credential : 비밀번호(password)
Spring Security의 특징
- Filter를 기반으로 동작한다
- Spring MVC와 분리되어 관리하고 동작할 수 있다
- Bean으로 설정할 수 있다
- Spring Security 3.2부터는 XML 설정을 하지 않아도 된다
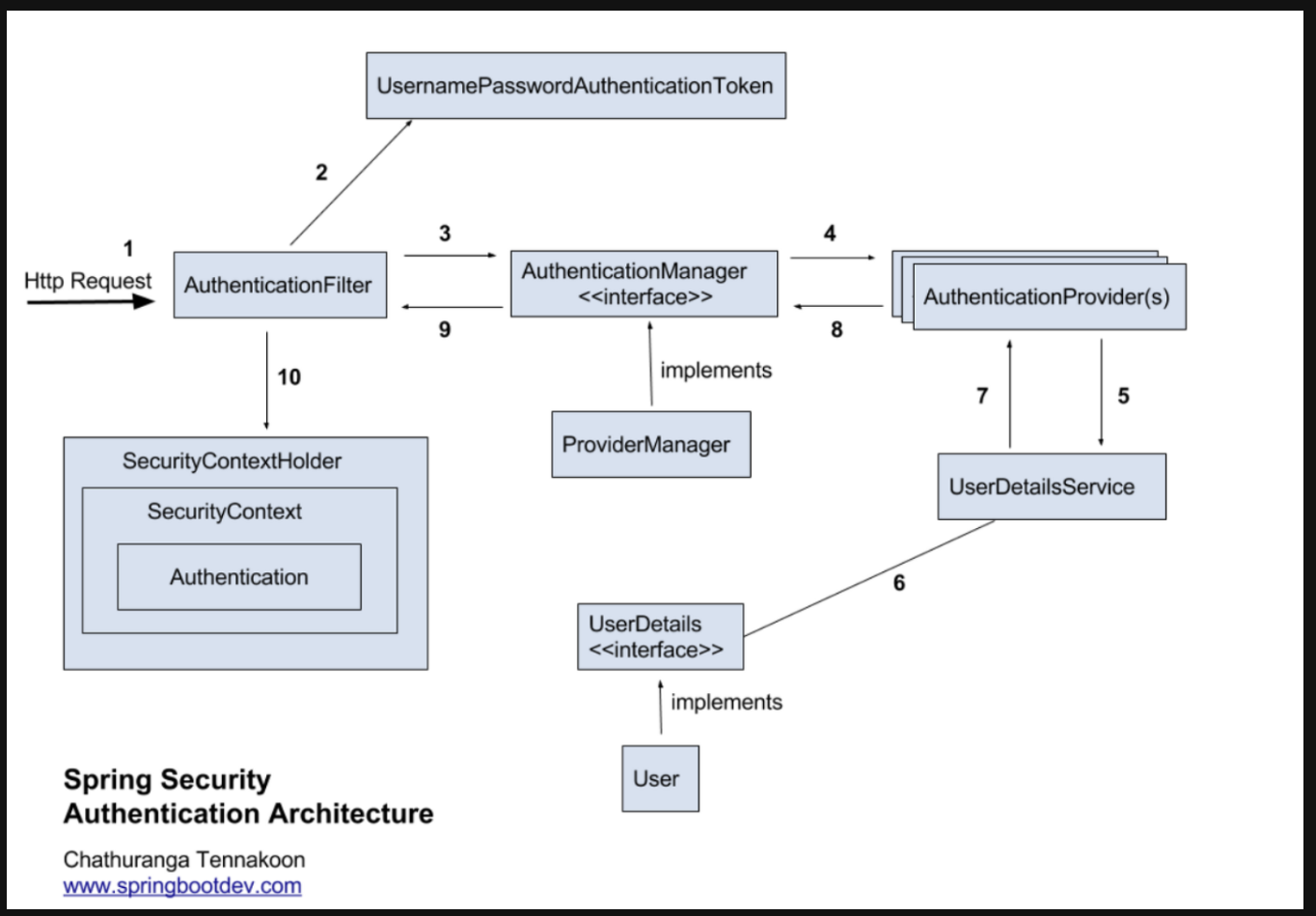
- 사용자가 폼에 아이디, 패스워드를 입력하면 HTTPServletRequest에 아이디, 비밀번호 정보가 전달된다. 이때, AuthenticationFilter가 넘어온 아이디와 비밀번호의 유효성 검사를 실시한다.
- 유효성 검사 후 실제 구현체인 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 만들어 넘겨준다
- 인증용 객체인 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 AuthenticationManager에게 전달한다
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 AuthenticationProvider에게 전달한다
- 사용자 아이디를 UserDetailsService로 보낸다. UserDetailsService는 사용자 아이디로 찾은 사용자의 정보를 UserDetails 객체로 만들어 AuthenticationProvider에게 전달한다.
- DB에 있는 사용자 정보를 가져온다
- 입력 정보와 UserDetails의 정보를 비교해 실제 인증 처리를 진행한다
- ~10까지 인증이 완료되면, SecurityContextHolder에 Authentication을 저장한다. 인증 성고 여부에 따라 성공 시 AuthenticationSuccessHandler, 실패 시 AuthenticationFailureHandler를 실행한다.
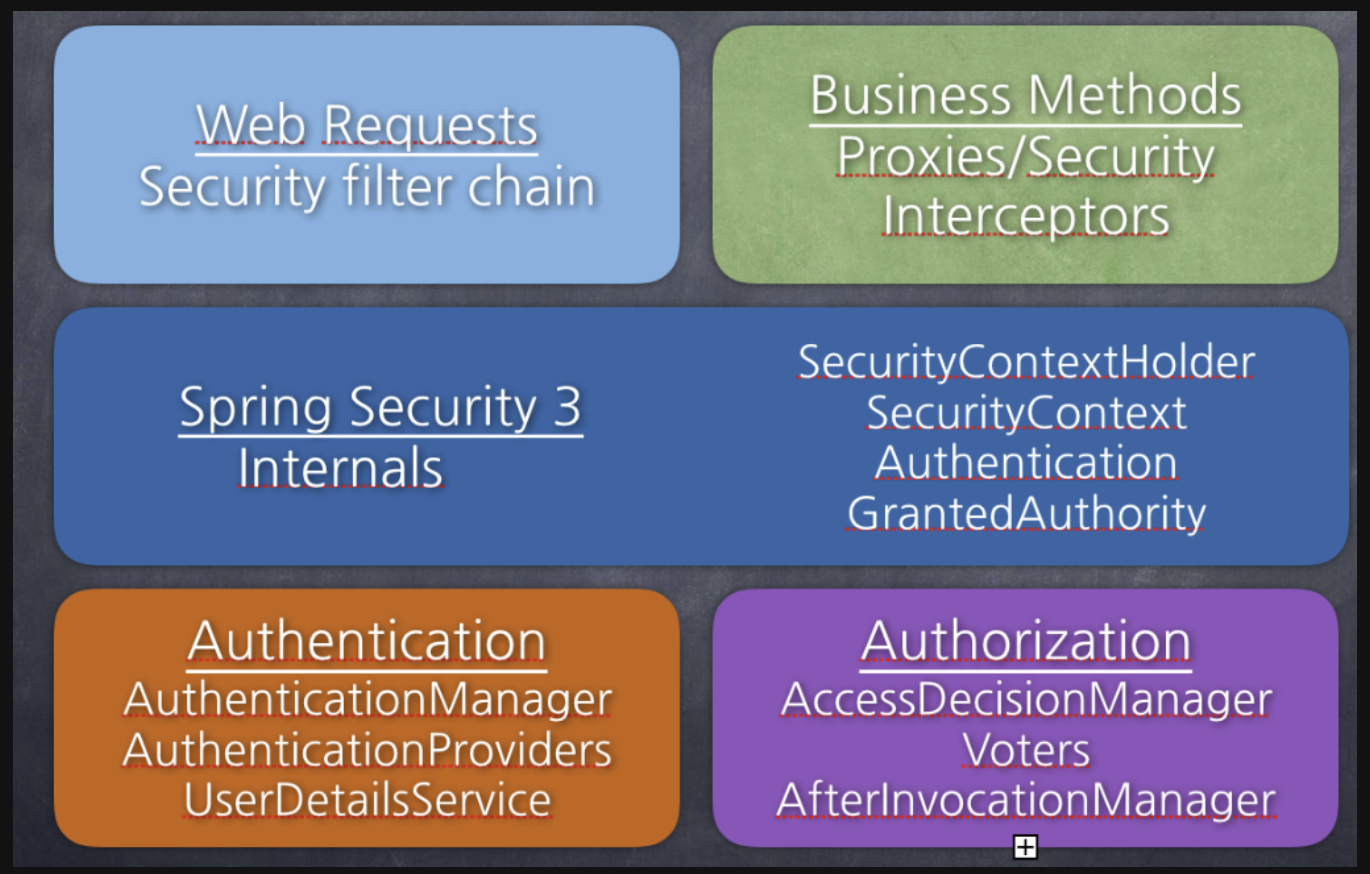
Spring Security의 주요 모듈
- 1.. SecurityContextHolder, SecurityContext, Authentication
- 유저의 아이디와 패스워드 사용자 정보를 넣고 실제 가입된 사용자인지 체크한 후 인증에 성공하면 우리는 사용자의 principal과 credential 정보를 Authentication안에 담는다
- 스프링 시큐리티에서 방금 담음 Authentication을 SecurityContext에 보관한다. 이 SecurityContext를 SecurityContextHolder에 담아 보관한다
- Authentication 클래스는 현재 접근하는 주체의 정보와 권한을 담는 인터페이스
- SecurityContext에 저장되며, SecurityContextHolder를 통해 SecurityContext에 접근
- SecurityContext를 통해 Authentication에 접근할 수 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable{
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
Object getCredentials();
Object getDetails();
Object getPrincipal();
boolean isAuthenticated();
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
- 우리가 로그인한 사용자의 정보를 얻기 위해서
- SecurityContextHolder.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
- 이 구문을 사용하여 가져오는 이유이다.
- 2.. UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
- 이 클래스는 Authentication을 구현한 AbstractAuthenticationToken의 하위의 하위클래스이다.
- 유저의 ID가 principal의 역할을 하고 유저의 password가 credential 역할을 한다
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken의 첫번째 생성자는 인증 전에 객체를 생성하고, 두번째는 인증이 완료된 객체를 생성한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationToken implements Authentication, CredentialsContainer{
}
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken{
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
// 인증 완료 전의 객체 생성
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials){
super(null);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
setAuthenticated(false);
}
// 인증 완료 후의 객체 생성
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities){
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
super.setAuthenticated(true); // must use super, as we override
}
}
- 3.. AuthenticationManager
- 인증에 대한 부분은 이클래스를 통해서 처리가 된다
- 실질적으로는 AuthenticationManager에 등록된 AuthenticationProvider에 의해서 처리가 된다
- 인증에 성공하면 두번째 생성자를 이용해 생성한 객체를 SecurityContext에 저장한다
1
2
3
public interface AuthenticationManager{
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
}
- 4.. AuthenticationProvider
- 이 클래스는 실제 인증에 대한 부분을 처리하는 작업을 치룬다.
- 인증 전에 Authentication 객체를 받아 인증이 완료된 객체를 반환하는 역할을 하고 아래와 같은 인터페이스를 구현해 Custom한 AuthenticationProvider를 작성하고
- AuthenticationManager에 등록하면 된다
1
2
3
4
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
- 5.. ProviderManager
- AuthenticationManager를 구현한 ProviderManager는 AuthenticationProvider를 구성하는 목록을 갖는다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware, InitializingBean {
public List<AuthenticationProvider> getProviders() {
return this.providers;
}
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
// for문으로 모든 provider를 순회하여 처리하고 result가 나올때까지 반복한다.
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) { ... }
}
}
- 6.. UserDetailsService
- 이 클래스는 UserDetails 객체를 반환하는 하나의 메소드만을 가지고 있다
- 일반적으로 이를 구현한 클래스에서 UserRepository를 주입받아 DB와 연결하여 처리한다.
1
2
3
public interface UserDetailsService{
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
- 7.. UserDetails
- 인증에 성공하여 생성된 UserDetails 클래스는 Authentication 객체를 구현한 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 생성하기 위해 사용된다
- UserDetails를 구현하여 처리할 수 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable{
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}
- 8.. SecurityContextHolder
- SecurityContextHolder는 보안 주체의 세부 정보를 포함하여 응용 프로그램의 현재 보안 컨텍스트에 대한 세부 정보가 저장된다
- 9.. SecurityContext
- Authentication을 보관하는 역할을 하며, SecurityContext를 통해 Authentication을 저장하거나 꺼내올 수 있다.
- SecurityContextHolder.getContext().set or get Authentication(authenticationObject);
- 10.. GrantedAuthority
- GrantedAuthority는 현재 사용자(Principal)가 가지고 있는 권한을 의미한다.
- ROLE_ADMIN, ROLE_USER 와 같이 ROLE_* 의 형태로 사용한다
- GrantedAuthority 객체는 UserDetailsService에 의해 불러올 수 있고, 특정 자원에 대한 권한이 있는지 없는지를 검사해 접근 허용 여부를 결정한다